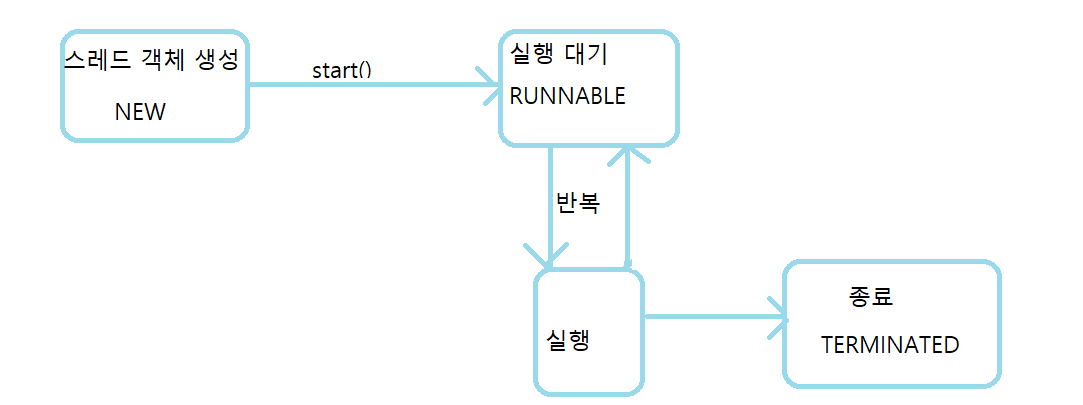
스레드 상태?

스레드 객체를 생성하고 start() 메소드를 호출하면 바로 실행되는 것이 아니라 실행 대기 상태가 된다.
운영체제는 실행 대기 상태에 있는 스레드 중 하나를 선택해 실행 상태로 만든다.
실행 대기 상태에 있는 스레드 중 OS는 하나의 스레드를 선택하고 CPU(코어)가 run() 메소드를 실행하도록 한다
이 때를 실행(running)상태라고 부른다
실행상태의 스레드는 run()메소드를 모두 실행하기전 다시 실행대기상태로 돌아갈 수 있으며, 실행대기 상태에 있는 다른 스레드가 선택되어 실행상태가 될 수도 있다.
이렇게 실행 대기, 실행 상태를 번갈아가며 run()메소드를 실행한다. 실행상태에서 run()메소드가 종료되면 더 이상 실행할 없기 때문에 스레드의 실행은 멈추게되고 이 상태를 종료(terminated)상태 라고 한다
스레드 상태제어
멀티 스레드 중 실행중인 스레드의 상태를 변경하는 것
ex) 미디어플레이어에서 동영상을 보다가 일시정지 또는 종료상태로 만드는 것
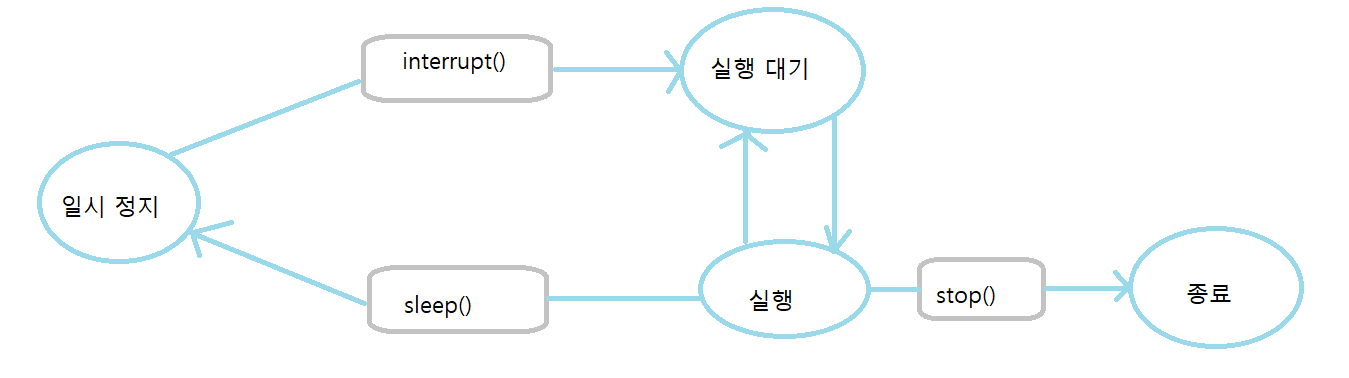
| 메소드 | 설명 |
| interrupt() | 일시 정지 상태의 스레드에서 InterruptedException을 발생시켜, 예외처리코드(catch)에서 실행대기 상태로 가거나 종료 상태로 갈 수있도록 한다 |
| sleep(long millis) | 주어진 시간동안 스레드를 일시 정지 상태로 만든다. 주어진 시간 후에는 자동실행하여 대기상태가 된다 |
| stop() | 스레드를 즉시 종료한다. 불안전한 종료를 유발하므로 사용하지 않는것을 추천한다 |
스레드의 안전한 종료
public class PrintThread1 extends Thread{
private boolean stop;
public void setStop(boolean stop) {
this.stop = stop;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (!stop) {
System.out.println("실행 중");
}
System.out.println("자원 정리");
System.out.println("실행 종료");
}
}public class StopFlagEx {
public static void main(String[] args) {
PrintThread1 printThread1 = new PrintThread1();
printThread1.start();
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {}
printThread1.setStop(true);
}
}
stop 필드가 true일 경우 while문의 조건식이 false가 되어 while문을 빠져나온다. 그리고 스레드가 사용한 자원을 정리하고, run()메소드가 끝나 안전하게 종료된다.
다른 방법으로는 interrupt()메소드를 이용할 수 있다
public class PrintThread2 extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
try {
while (true) {
System.out.println("실행 중");
Thread.sleep(1); //일시정지 시 main메소드에서 예외발생
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {}
System.out.println("자원 정리");
System.out.println("실행 종료");
}
}public class InterruptEx {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread = new PrintThread2();
thread.start();
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO: handle exception
}
//스레드를 종료하기위해 InterruptedException 발생시킴
thread.interrupt();
}
}
주의할점은 스레드가 실행대기 또는 실행 상태에 있을 때 interrupt() 메소드가 실행되면 즉시 예외가 발생하는것이아닌 스레드가 미래에 일시정지 상태가 되면 InterruptedException이 발생한다는 것
그래서 Thread.sleep(1)을 사용함
일시정지를 만들지 않고도 interrupt()호출여부를 알고싶다면
interrupted() 또는 isInterrupted()메소드를 확인한다.
둘의 차이는 정적메소드, 인스턴스 메소드이다
public void run() {
while (true) {
System.out.println("실행 중");
if(Thread.interrupted()) {
break;
}
}
System.out.println("자원 정리");
System.out.println("실행 종료");
}
데몬스레드?
주 스레드의 작업을 돕는 보조역할을 수행하는 스레드
주 스레드가 종료되면 데몬 스레드는 강제적으로 자동종료된다
ex) 워드프로세서 자동저장, 쓰레기수집기 등 은 주 스레드인 워드프로세서나 JVM이 종료되면 같이종료됨
스레드를 데몬으로 만들기 위해서는 주 스레드가 데몬이 될 스레드의 setDaemon(true)를 호출해 주면된다
public static void main(String[] args){
AutoSaveThread thread = new AutoSaveThread();
thread.setDaemon(true);
thread.start();
...
}위 코드는 main스레드가 주 스레드 AutoSaveThread가 데몬 스레드가 된 예제이다.
주의할 점
start()메소드 호출 후 setDaemon메소드를 호출하면 IllegalThreadStateException이 발생 (순서주의)
현재 실행중인 스레드가 데몬스레드인지 아닌지 구별하려면 isDaemon()메소드의 리턴값이 true인지 확인해보면 된다.
public class AutoSaveThread extends Thread{
public void save() {
System.out.println("작업 내용을 저장한다");
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
break;
}
save();
}
}
}public class DaemonEx {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AutoSaveThread autoSaveThread = new AutoSaveThread();
autoSaveThread.setDaemon(true); //AutoSaveThread를 데몬스레드로 만듦
autoSaveThread.start();
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
System.out.println("메인 스레드 종료");
}
}1초 주기로 save()메소드를 자동호출하도록 AutoSaveThread를 작성하고
메인스레드가 3초후 종료되면 AutoSaveThread도 같이 종료되도록 AutoSaveThread를 데몬스레드로 만들었다

참고 :
- 혼자 공부하는 자바(신용권), 한빛미디어
'개발 > JAVA' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Java] 컬렉션 프레임워크 - Map (0) | 2022.08.14 |
|---|---|
| [Java] 컬렉션 프레임워크 - List, Set (0) | 2022.08.14 |
| [Java] 멀티 스레드2 (0) | 2022.07.26 |
| [Java] 멀티 스레드 1 (0) | 2022.07.25 |
| [Java] java.util 패키지 내 Date, Calendar 클래스 (0) | 2022.07.21 |
